What is Periodic Accrual/Deferral in SAP FI and Why is it Important?
- Oznur Ozen

- Sep 25, 2025
- 2 min read

1. Introduction: The Concept of Accounting Periods
One of the fundamental principles of financial accounting is the periodicity principle. According to this principle, revenues and expenses must be recorded in the period to which they belong. For example, income earned in 2025 should be recorded in 2025, while parts extending into 2026 should be deferred to the relevant period. In the SAP FI module, the most important mechanism for applying this principle is the process of accruals and deferrals. 2. What is Accrual/Deferral?
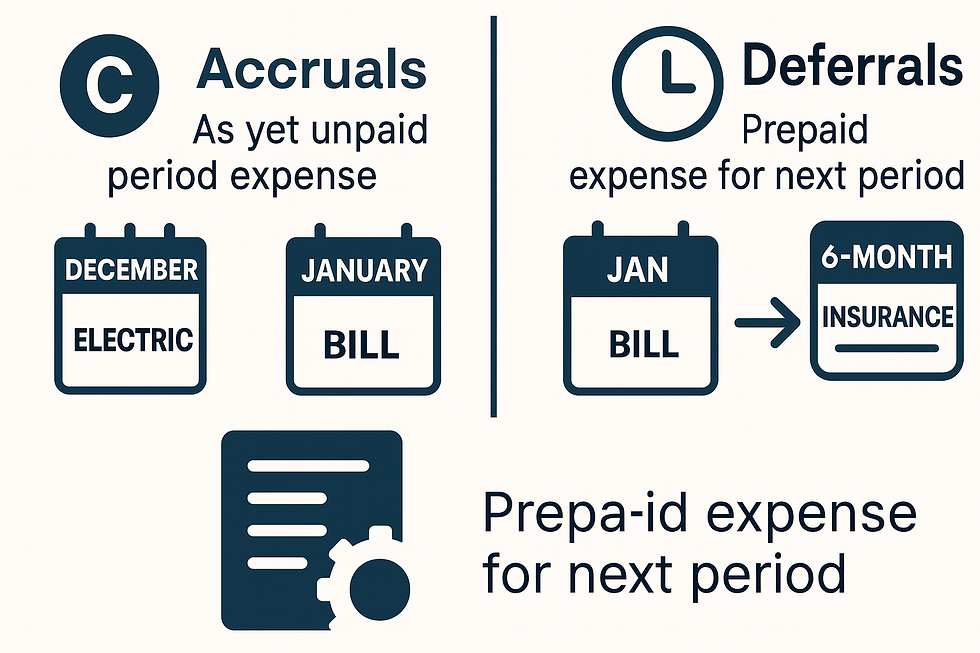
Accrual/deferral is the process of allocating revenues and expenses to the periods in which they actually occur, regardless of the actual cash movements.
- Accruals: Expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid. Example: Electricity consumption in December 2025, but the invoice arrives in January 2026. The expense must be accrued to December.
- Deferrals: Revenues/expenses that are prepaid but belong to future periods. Example: An insurance premium paid in advance for one year is distributed equally over 12 months.
3. Importance of Accrual/Deferral in SAP FI
- Accurate financial reporting: Ensures that the income statement and balance sheet reflect reality.
- Legal compliance: Meets the requirements of tax regulations and international accounting standards such as IFRS/US-GAAP.
- Better decision support for management: Makes the difference between cash flow and profit/loss statement more visible.
4. Accrual/Deferral Processes in SAP FI
a) Manual Accrual/Deferral
Users can distribute transactions manually via FI documents.- Example: Accrual posting via FB50 or FBS1.- Reversal and distribution with transactions F.81 and F.92.
b) Automatic Accrual/Deferral (Accrual Engine)
SAP automates the process using the Accrual Engine:
- Accrual and deferral postings are automatically generated by the system.
- Planned expenses/revenues (e.g., rent, insurance) are automatically distributed monthly.
- Reduces manual workload at period closing.
c) Innovations in S/4HANA
- The Accrual Engine now operates on the Universal Journal (ACDOCA). - Postings are fully integrated into FI-GL within a single table. - SAP Fiori apps make the process more user-friendly.
5. Example Scenarios - Rent Expense: An annual rent payment in January is distributed equally over each month. - Electricity Accrual: The December invoice arrives in January. SAP posts an accrual in December and reverses it in January .- Insurance Premiums: A yearly insurance premium is distributed monthly using the Accrual Engine.
6. Accrual/Deferral in Turkey Localization In Turkey, regulations such as the Tax Procedure Law (VUK) and TMS/TFRS standards require the periodic allocation of revenues and expenses. - Especially in e-Ledger (e-Defter) and financial closing processes, accrual/deferral plays a critical role. - Incorrect or missing accrual/deferral can result in significant audit findings.
7. Common Issues in Accrual/Deferral
- Wrong period selection → leads to inaccurate reports.
- Reversal forgotten → revenues/expenses may be counted twice.
- High error rate in manual processes → therefore, the use of the Accrual Engine is recommended.
8. Conclusion and Recommendations
Accrual/deferral in SAP FI is a fundamental process that ensures the accuracy of financial statements and compliance with regulations.
- In small companies, it may be done manually.
- In large and multinational companies, Accrual Engine + S/4HANA Universal Journal integration should be used.
For an FI consultant, knowing the accrual/deferral process well:
- Builds credibility during project implementations.
- Provides critical contributions at period-end closings.
- Makes a difference during audits.




Comments